What is the difference between lining and vulcanized valve seat?
There are three types of rubber seat. One is a soft seat, which can be installed and removed at will. It is elastic; the other is a backrest seat, which is a hard seat. The seat is knocked into the valve by external force. The body, but it can also be disassembled, which is much more laborious than the disassembly of the soft seat; the third type is the vulcanized seat, which uses high temperature vulcanization to fix the seat to the valve body, so the vulcanized seat is sometimes called a fixed liner.
D71J is a rubber-lined valve cavity and butterfly plate are lined with rubber, D71X only the sealing surface is rubber
D71J rubber lining is that the valve body and disc plate are all covered with rubber. This is generally used for
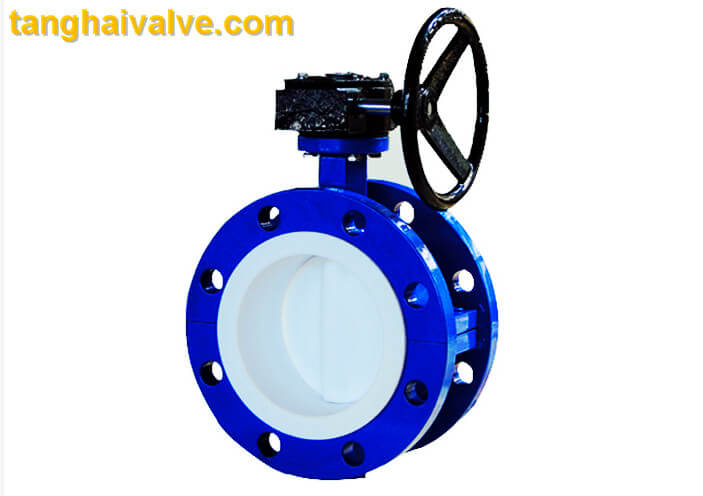

Double flange butterfly valve (10)
corrosive media.
And D71X means rubber seal. It’s just the soft seal we are talking about. This general medium takes a lot of water. This price is also much cheaper.
The rubber lining in the rubber lining butterfly valve is to use high temperature to vulcanize the rubber and the valve body at high temperature. It has very high corrosion resistance and is generally used to control some corrosive fluids with strong acid and alkali.
The rubber butterfly valve is a butterfly valve whose seal is a rubber seal, which is generally called a valve seat, and is separately installed into a whole.
At normal temperature, the abrasion resistance of natural soft rubber is much better than that of nitrile rubber, but their high temperature resistance is the highest limit within 80 degrees, and it is not suitable for use if it exceeds 80 degrees.
The difference between fully lined butterfly valve and half lined butterfly valve:
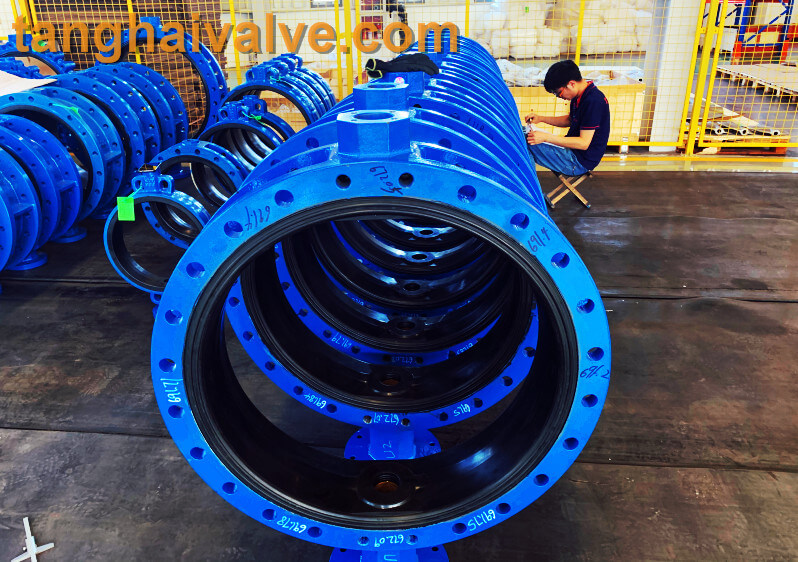

U type flange butterfly valve (9)
1. Semi-lined butterfly valve means: the butterfly valve is not lined with rubber, and the place where the butterfly valve is connected to the valve body is lined with rubber;
2. Fully lined butterfly valve means: the butterfly plate of the butterfly valve and the part connected with the valve body are lined with rubber.
The difference between rubber lined butterfly valve, fluorine lined butterfly valve and plastic lined butterfly valve: rubber lined butterfly valve and fluorine lined butterfly valve are only one kind of plastic lined butterfly valve.
The sealing materials in the rubber-lined butterfly valve are:
Hard rubber NR applicable temperature: -10℃~85℃,
Suitable temperature of soft rubber BR: -10℃~85℃,
Suitable temperature of butyl rubber IIR: -10℃~120℃,
Applicable temperature of neoprene CR: -10℃~105℃;
The sealing materials in the fluorine-lined butterfly valve are:
Polyperfluoroethylene FEP (F46) operating temperature: -85℃~150℃,
Polytetrachloroethylene PTFE (F4) operating temperature: -200℃~180℃,
Polytrifluoroethylene PCTEF (F3) operating temperature: -195℃~120℃,
Polypropylene: RPP operating temperature: -14℃~80℃,
Polyvinyl chloride: rigid) PVC service temperature: 0℃-55℃,
Polyvinylidene chloride PVDF (F2) operating temperature: -70℃~100℃,
Polyolefin: PO Operating temperature: -58℃~80℃.
TH Valve is a professional manufacturer of butterfly valve, gate valve, check valve, globe valve, knife gate valve, ball valve with API, JIS, DIN standard, used in Oil, Gas, Marine industry, Water supply and drainage, fire fighting, shipbuilding, water treatment and other systems, with Nominal Diameter of DN50 to DN1200, NBR/EPDM/VITON, Certificates & Approvals: DNV-GL, Lloyds, DNV, BV, API, ABS, CCS. Standards: EN 593, API609, API6D
Related news/knowledge:
Code of valve sealing or lining material;
Valve seat sealing (TH-VSE);
Description of lining material for rubber lining valve;
Lining material and its application scope of fluorine lined valve















 © Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
© Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.